The United States witnessed a remarkable shift toward home gardening in 2023, reflecting a deeper commitment to sustainability and self-reliance. Dive into the comprehensive statistics that highlight this burgeoning movement.
Contents
- Number of Home Food Growers
- Historical Context
- Who Gardens?
- Home Gardeners Are Increasing
- Good for Mental Health
- Gardening Saves Money
- Popular Home-Grown Veggies
- Community Gardening
Home Food Growers by the Numbers
Growing one’s own food has seen a significant uptick in the U.S. With the rise of sustainable living and the benefits of fresh produce, more Americans are turning to their backyards and balconies to cultivate crops.
- 67% of adults in the U.S. are growing or planning to grow edible plants.
- 42% have started growing their own produce.
- Over 2 in 5 U.S. households are now growing food.
The trend of growing one’s own food, driven by sustainable living and the appeal of fresh produce, has gained momentum in the U.S.
Currently, 67% of U.S. adults are involved or intend to cultivate edible plants, with 42% already producing their own food. This means more than two out of every five American households practice home-based agriculture.
Historical Context
Comparing the current trend with past years provides a clearer picture of the rapid growth in home gardening. The data from 2019 serves as a benchmark, showing how the movement has evolved over a few short years.
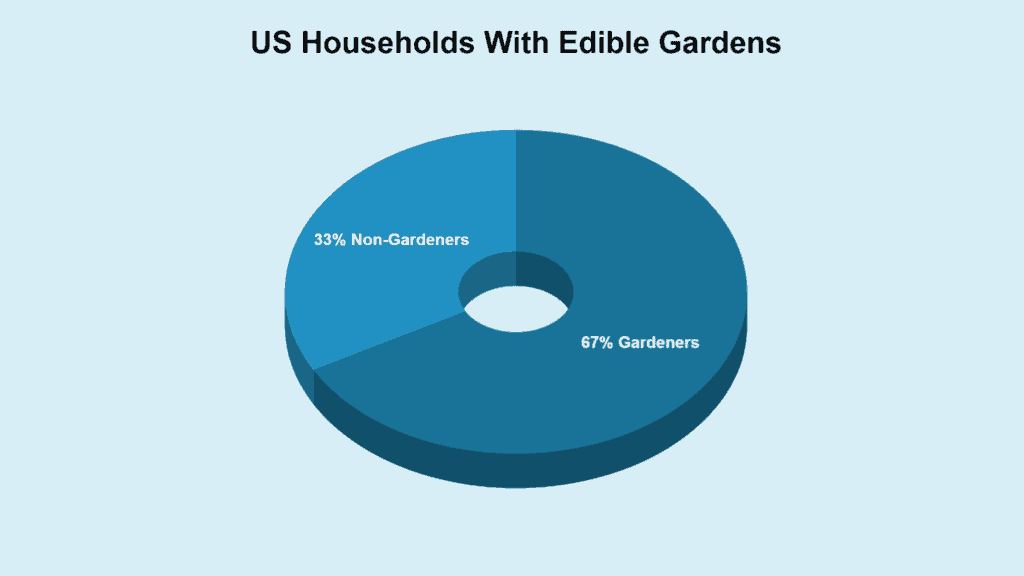
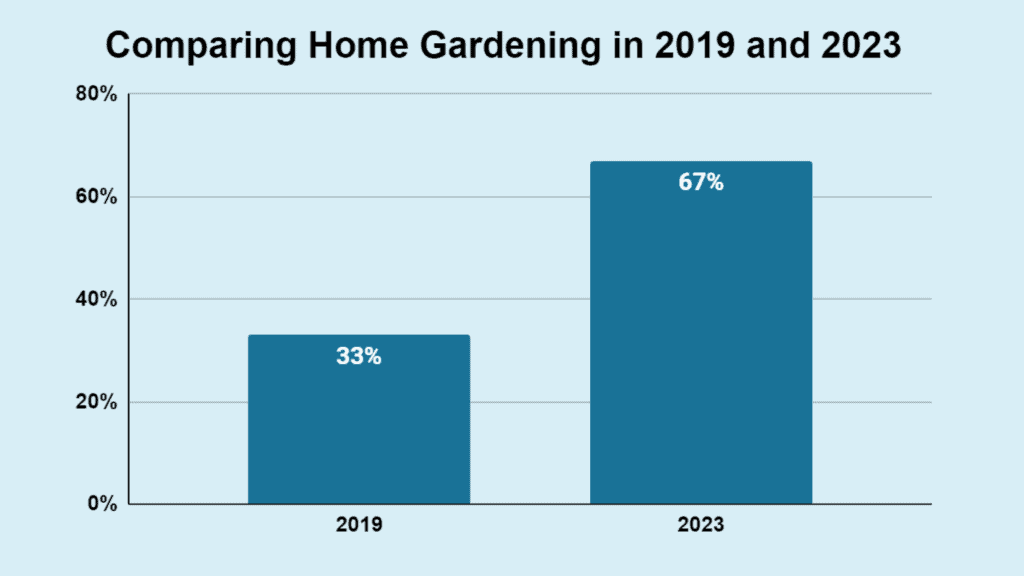
In 2019, 33% of U.S. homes reported food gardening. This indicates that approximately one-third of U.S. households were engaged in growing their own food that year.
| Year | Edible Gardens | Non-Gardeners |
|---|---|---|
| 2019 | 33% | 67% |
| 2023 | 67% | 33% |
Analyzing the present trend against previous years offers insight into the swift expansion of home gardening. Using 2019 data as a reference point, we can observe the evolution of this movement in just a brief span.
Back in 2019, about one-third of U.S. households, or 33%, confirmed their involvement in food gardening, highlighting the portion of Americans growing their own food at that time.
It’s interesting to note that, over the last five years, the percentage of gardeners with edible plants has reversed.
Source: FOX 10 Phoenix
Demographics
The demographics of home gardeners offer insights into which segments of the population are most actively participating.
Families, in particular, are leading the charge, with regions across the U.S. showcasing varying levels of engagement.
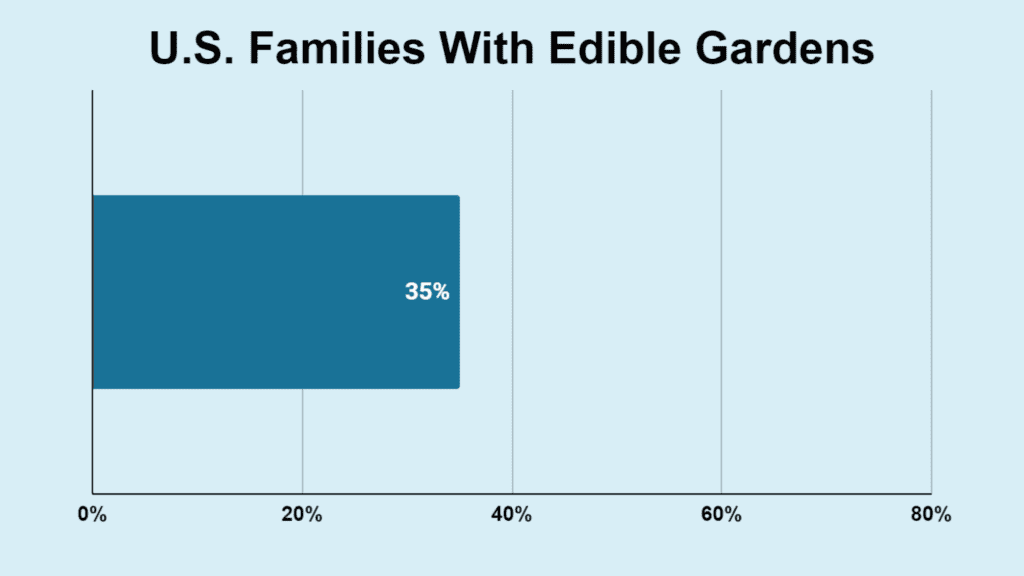
- 35% of families in the U.S. are actively involved in growing vegetables, fruits, and other foods.
- About 25% of households have gardens.
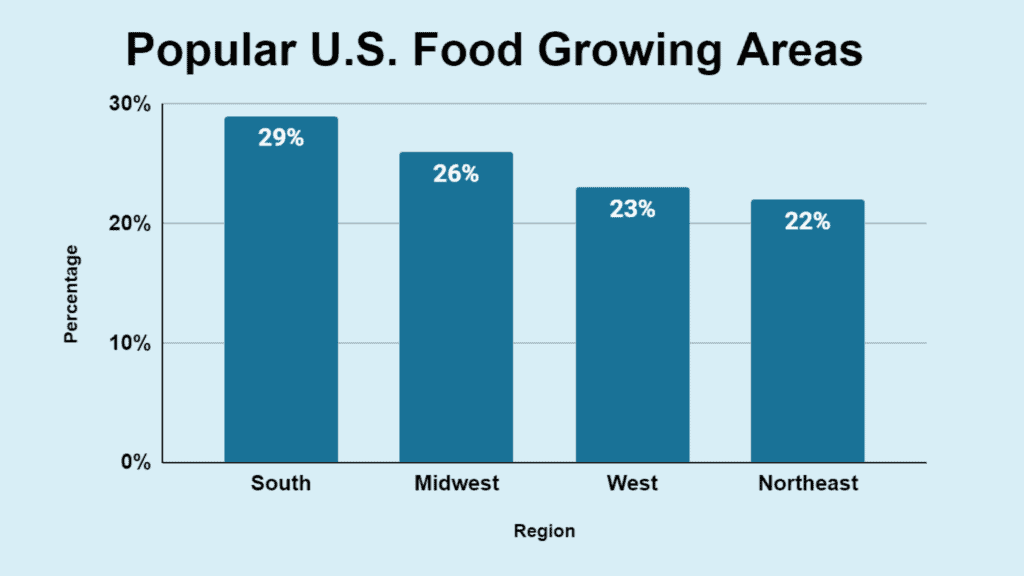
- Regional breakdown: South (29%), Midwest (26%), West (23%), and Northeast (22%).
Which part of the United States has the most food growers?
| Region | Garden Growers |
|---|---|
| Northeast | 22% |
| West | 23% |
| Midwest | 26% |
| South | 29% |
The profile of home gardeners sheds light on the specific population groups that are most engaged. Notably, families stand out as the primary participants in this movement.
Different regions in the U.S. display diverse levels of involvement. Currently, 35% of American families actively cultivate vegetables, fruits, and other edibles, while roughly 25% of all households maintain gardens.
Home Garden Growth Over the Last 5 Years
The evolution of home gardening over the past half-decade reveals a society increasingly valuing self-sufficiency and organic produce. The reasons for this growth are multifaceted, with global events playing a significant role.
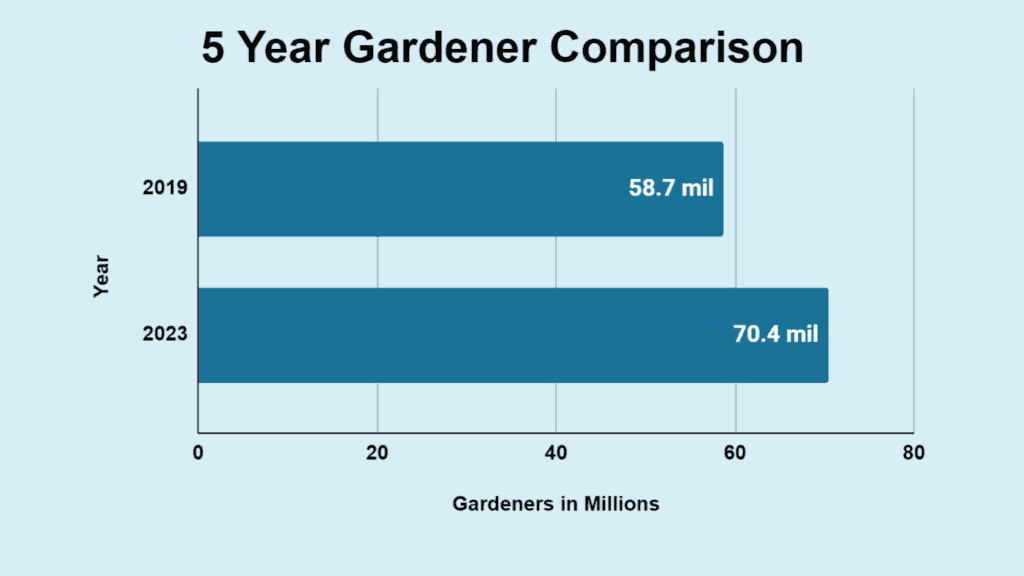
- The approximate number of gardeners in 2019 was 58.7 million.
- The estimated number of gardeners in 2023 was 70.4 million.
- Over the last five years, there was a 20% increase in households initiating gardens or 11.7 million gardeners.
- Growth is attributed to factors like the global pandemic and some distinct advantages.
| Year | Gardeners in Millions |
|---|---|
| 2023 | 70.4 mil |
| 2019 | 58.7 mil |
Home gardening has surged over the past five years, reflecting a societal shift toward self-reliance and organic produce. Influenced by events like the global pandemic, the number of gardeners rose from 58.7 million in 2019 to an expected 70.4 million in 2023.
This represents a 20% increase, or 11.7 million new gardeners, highlighting the growing appeal and benefits.
Source: Garden Pals
Mental Health Benefits
Beyond the tangible benefits of fresh produce, gardening offers therapeutic advantages. Nurturing plants and connecting with the earth profoundly affects mental well-being, providing a respite from the stresses of daily life.
- Gardening is linked to reductions in depression, anxiety, and body mass index.
- 49% of participants engaged in gardening because it improves mental health.
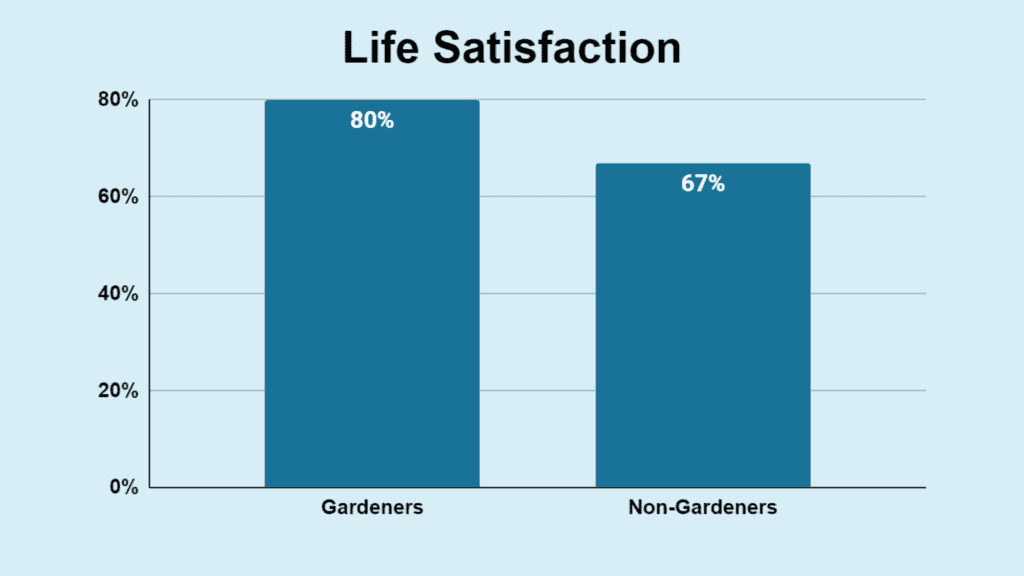
- 80% of gardeners felt “satisfied” with their lives compared to 67% of non-gardeners.
| Mental Health | |
|---|---|
| Gardeners | 80% satisfied with life |
| Non-Gardeners | 67% satisfied with life |
Gardening offers more than just fresh produce; it’s a therapeutic activity that positively impacts mental health. It’s linked to reduced depression, anxiety, and body mass index.
About 49% of gardeners cite mental health improvement as a reason to garden, and 80% feel content with their lives, compared to 67% of non-gardeners.
Financial Benefits
In an era of rising living costs, growing one’s own food offers a practical way to save on grocery bills. The financial benefits of gardening are becoming increasingly apparent, making it an attractive option for many households.
- 85% of Americans cited financial savings as a primary reason for starting their gardens.
- The average garden yields $600 of produce in a year. When subtracting the $70 spent per household on gardening, there is a return of about $530 yearly from the garden.
- The average size of an American vegetable garden is 600 sq. ft. A standard garden yields roughly $1 per sq. ft. in produce value.
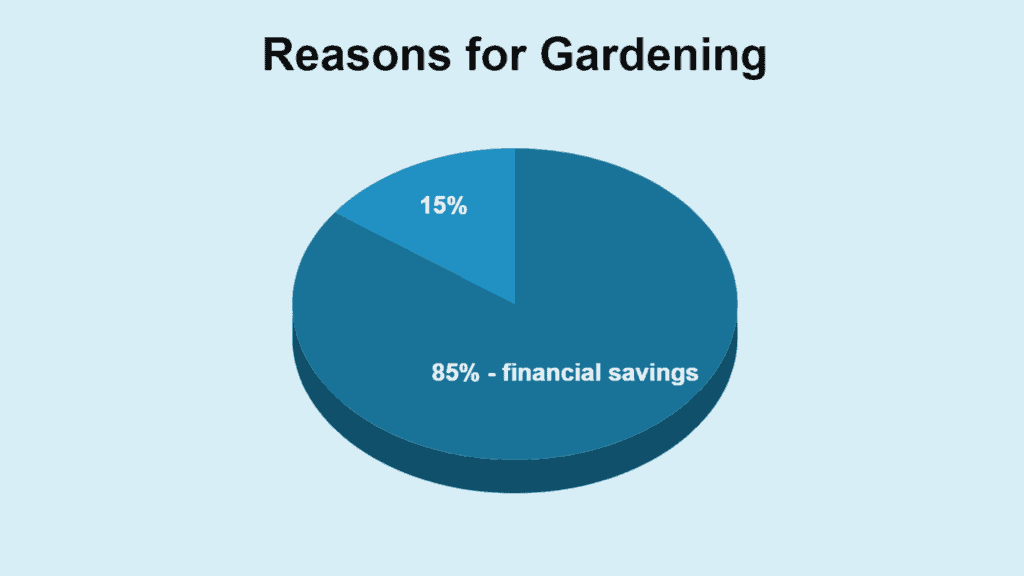
Amidst rising living costs, cultivating one’s own food has become a cost-effective choice for many. With 85% of Americans highlighting financial savings as a gardening motivation, the numbers speak for themselves.
A garden typically yields $600 in produce annually, and after a $70 investment, households see a net profit of $530. The average American vegetable garden, measuring 600 sq. ft., produces value at roughly $1 per sq. ft.
Sources: Garden Pals, Cooped Up Life, GreenPal
Most Popular Home-Grown Veggies
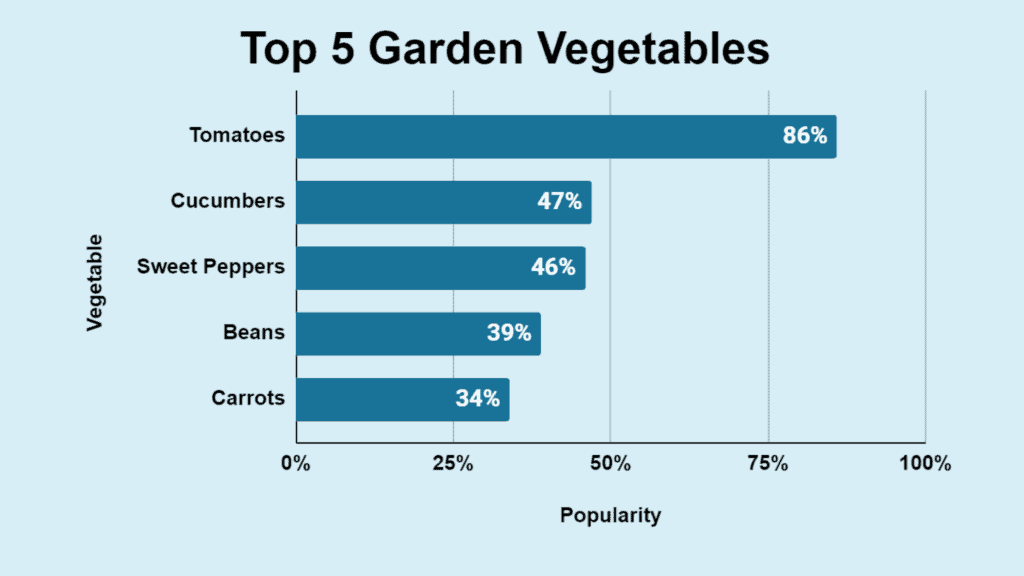
- Tomatoes are the most popular vegetable grown by U.S. gardeners, with 86% cultivating this fruit.
- 47% of gardeners grow cucumbers.
- Sweet peppers are grown by 46% of U.S. gardeners.
- Beans are grown by 39% of gardeners.
- 34% of gardeners grow carrots in their gardens.
| Vegetable | Popularity |
|---|---|
| Tomatoes | 86% |
| Cucumbers | 47% |
| Sweet Peppers | 46% |
| Beans | 39% |
| Carrots | 34% |
These statistics highlight the preference for vegetables that are easy to grow, versatile, and can be used in numerous dishes.
Source: Garden Pals
Community Gardens in the U.S.
A community garden is a shared space where individuals collaborate to cultivate plants, often in urban settings where personal garden space is scarce.
These gardens offer participants access to fresh produce, foster social interactions, and serve as educational platforms about gardening and nutrition.
They also provide environmental benefits by reducing urban heat islands, symbolizing communal effort, sustainability, and a connection to nature amidst urban landscapes.
- Over 18,000 community gardens in 2023, up from about 17,143 five years ago.
- 5% growth in community gardens since 2019.
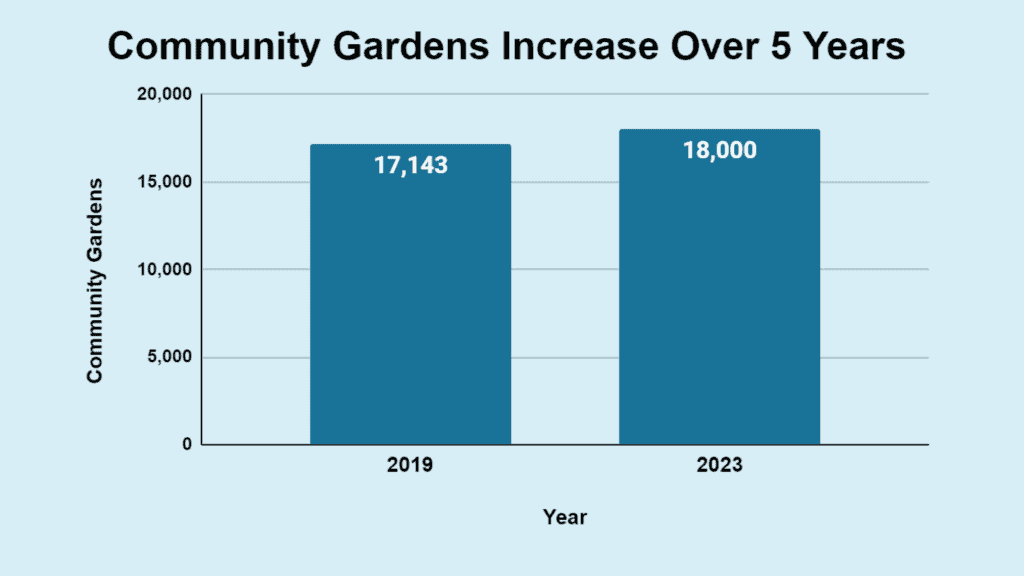
| Year | Number of Community Gardens |
|---|---|
| 2019 | 17,143 |
| 2023 | 18,000 |
Community gardens provide fresh produce, enhance community ties, and educate on gardening and nutrition. They combat urban heat and symbolize community-driven sustainability in cities. In 2023, community gardens increased to 18,000 from 17,143 in 2018, marking a 5% growth since 2019.
Conclusion
The gardening trend in the U.S. for 2023 reflects a broader movement toward sustainability, health, and community. As more Americans recognize the multifaceted benefits of growing their own food, this trend is poised to shape the nation’s food and health landscape in the years to come.
More Research
Uncovering the motivations and challenges faced by those taking control of their food sources is particularly relevant when considering the increasing number of US households opting to rent.
The shift toward remote work adds another layer to this conversation, highlighting the evolving relationship between our living spaces, work lives, and food cultivation practices.