The tiny home movement has gained significant traction in the United States over the past few years, with more and more people opting for a simpler, more sustainable way of living.
In this article, we explore the current state of the tiny home market in the U.S., including the number of tiny houses, their demographics, and the financial benefits of tiny living.
Contents
- Counting U.S. Tiny Homes
- States Where Tiny Homes Are Popular
- Market Size
- Would You Live in a Tiny Home?
- Cost of a Tiny House
- Cost by Square Foot
- Demographics for Tiny Homeowners
- Men vs Women
- Tiny Homeowner Income Stats
- Do Those With a Tiny Home Have a Mortgage?
- Financial Stability – Tiny Homeowners
- Reselling a Tiny Home
Tiny Home Numbers in the U.S.
The increasing popularity of tiny living is evident in the number of tiny homes, which is derived from data on sales and construction by certified builders.
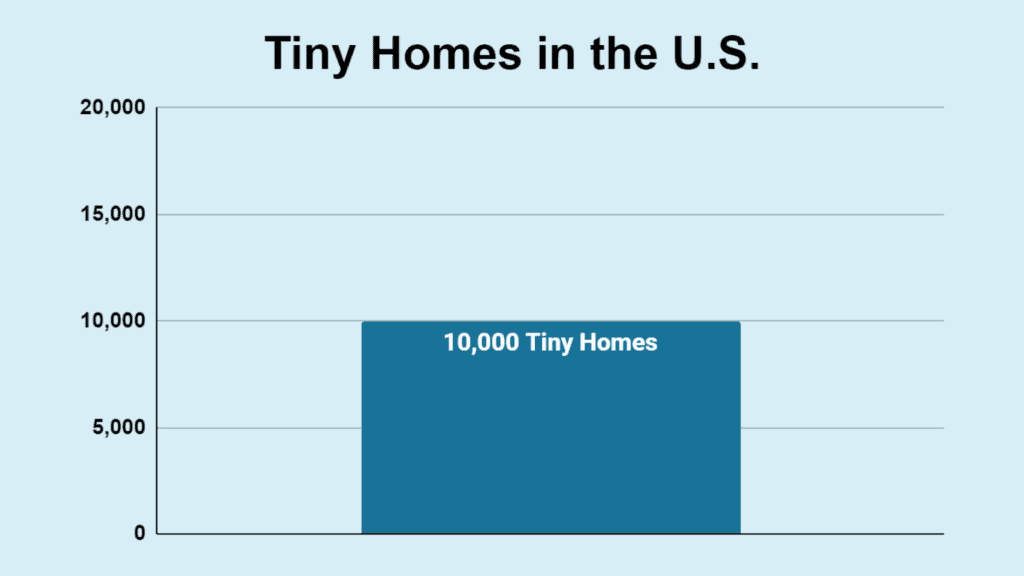
- In the United States, there are an estimated 10,000 tiny homes. However, this number is likely an underestimate, as many individuals who embrace the tiny living lifestyle opt to live off the grid and may not participate in surveys or register their homes, resulting in a higher actual number.
- Eleven states do not have statewide residential building codes.
- Tiny homes produce 2,000 pounds less CO2 emissions yearly than an average-sized home.
- Tiny homes are typically 100 to 400 square feet, compared to the average size of a traditional house in the U.S., which is about 1,900 square feet.
- The average square footage of a tiny home is 225 square feet.
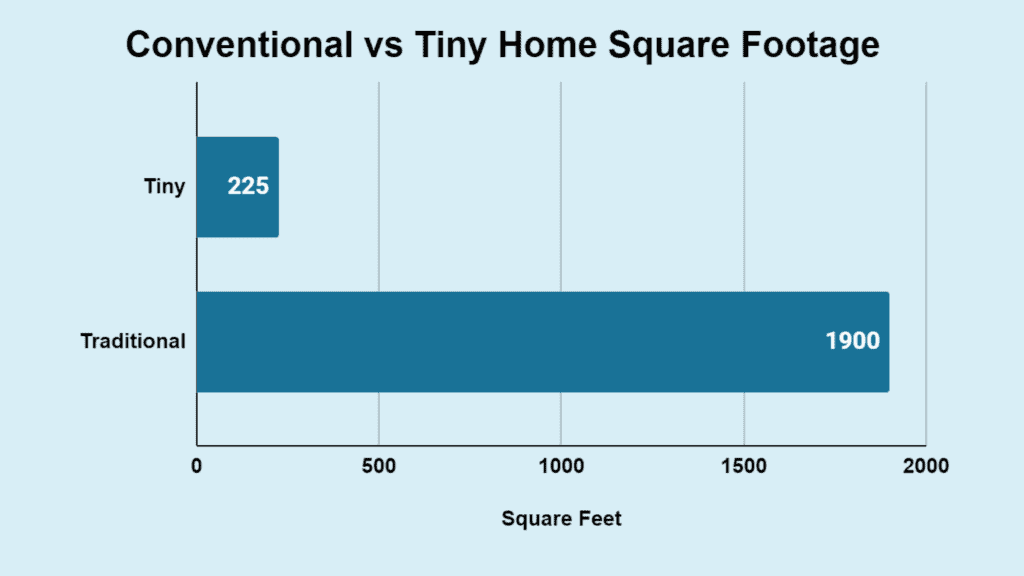
| Type of House | Home Size |
|---|---|
| Standard Home | 1900 square feet |
| Tiny House | 225 square feet |
Sources: Oregon Department of Environmental Quality, GoDownsize, U.S. Census Bureau, BobVila.com, The Tiny Life
Most Popular States for Tiny Homeowners
Tiny homeowners are more abundant in these states:
| Ranking | State |
|---|---|
| 1. | Oregon |
| 2. | California |
| 3. | Texas |
| 4. | North Carolina |
| 5. | Florida |
Source: Gitnux
Tiny House Market
The global tiny home market was valued at USD 18,467.38 million in 2023. It is expected to grow at a CAGR of 8.43%, reaching USD 30,018.52 million by 2030.
The North American region, which includes the United States, is estimated to account for 57% of the growth in the tiny homes market from 2022 to 2027.
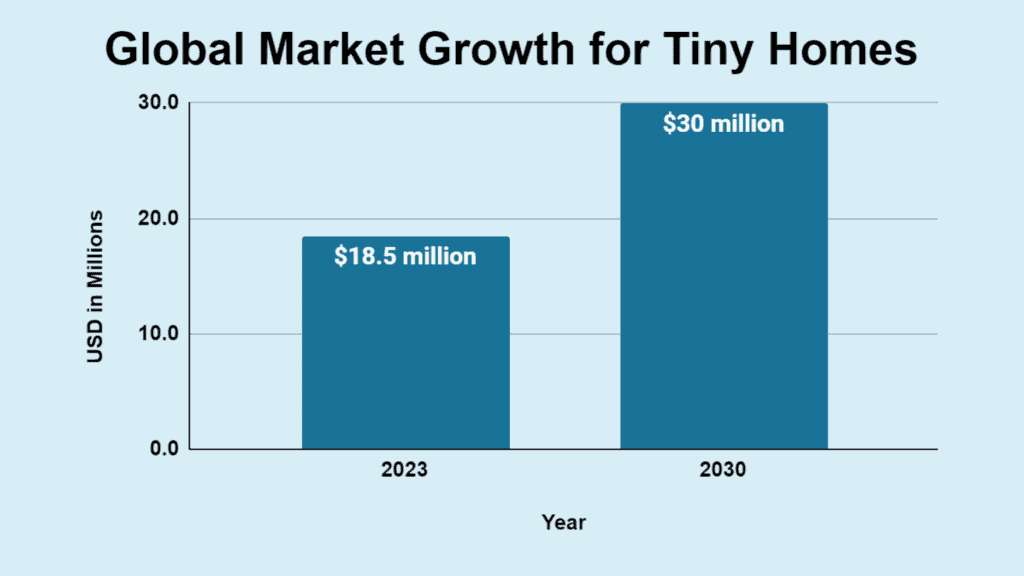
| Year | U.S. Dollars |
|---|---|
| 2023 | $18.5 million |
| 2030 | $30 million |
Source: Technavio, Yahoo! Finance, PRNewswire
Tiny Home Popularity
A survey conducted by a Fidelity National subsidiary discovered that 56% of Americans would consider living in a tiny home, while 24% would not, citing affordability and efficiency as the main reasons. This shows a significant interest in tiny living.
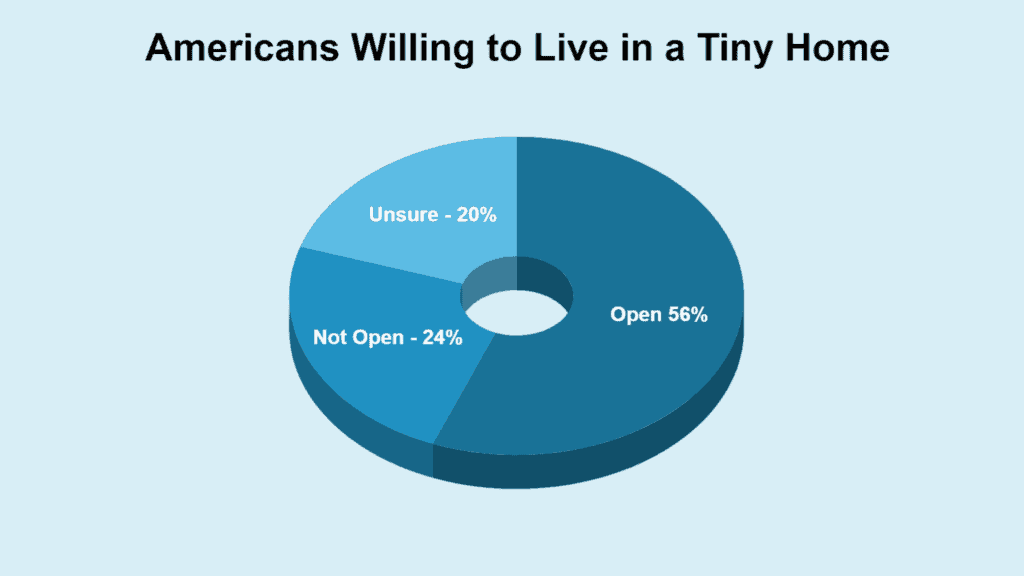
| Potential Tiny Home Dwellers | Percentage |
|---|---|
| Yes | 56% |
| No | 24% |
| Maybe | 20% |
Tiny Home Cost
Tiny houses are becoming an option for those seeking an affordable and eco-friendly living solution. Tiny house prices can vary widely, with averages falling between the low to mid-five figures. Still, it can range from very budget-friendly choices to more luxurious, feature-rich models with a higher price tag.
Custom-built tiny homes tend to be pricier, while prefab tiny homes provide a more economical alternative, with many price points to fit different budgets.
- A tiny house costs, on average, between $30,000 and $60,000. They can be as low as $8,000 or up to $150,000, depending on the amenities.
- Custom-built tiny houses cost $50,000 to $140,000, depending on the size and features.
- The price spectrum for prefab tiny homes is broad, starting as low as $4,000 and soaring up to $80,000 or more.
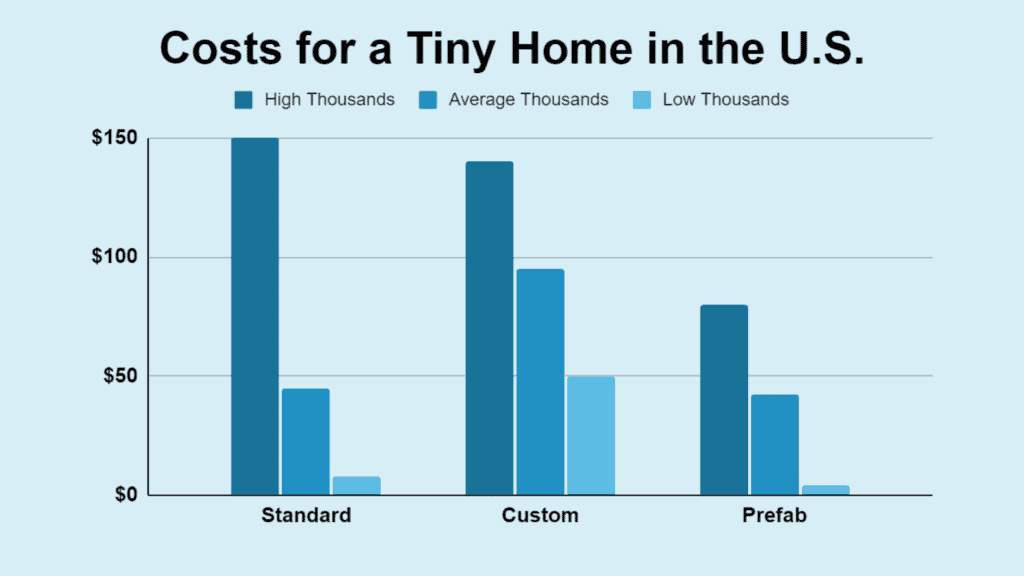
| Low | Average | High | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Prefab Tiny House | $4k | $42k | $80k |
| Standard Tiny House | $8k | $45k | $150k |
| Custom Tiny Home | $50k | $95k | $140k |
Sources: Rocket, Home Guide, Southwest Journal
Tiny Home Price Per Square Foot
Per square foot, tiny homes are 62% more expensive than traditional, full-sized homes. While tiny homes are generally cheaper overall, the cost per square foot is higher due to the need for compact and efficient design.
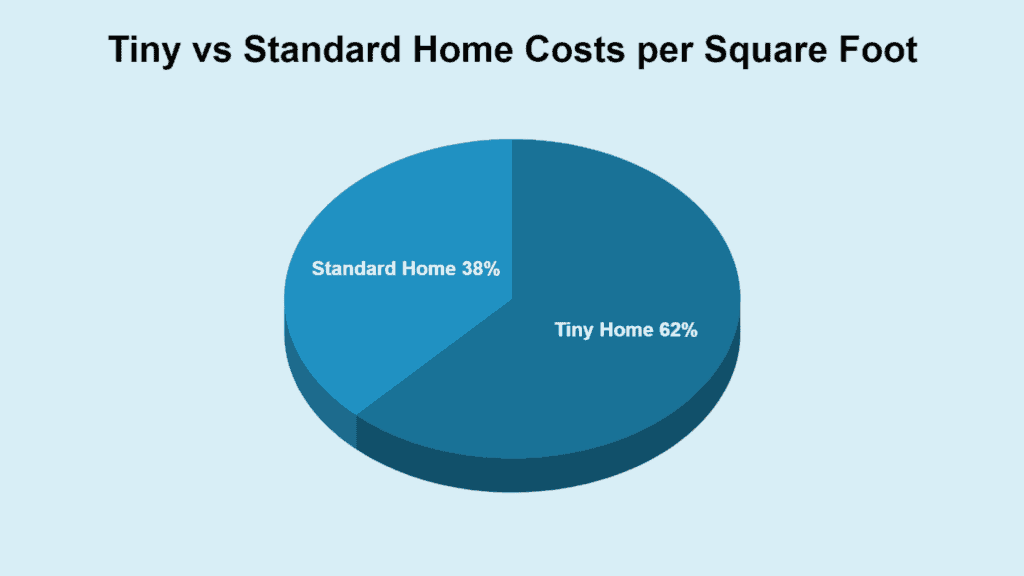
| House Type | Square Foot Costs |
|---|---|
| Traditional Home | 38% |
| Tiny House | 62% |
Source: Porch
Tiny Homeowner Demographics
The age distribution of tiny homeowners is pretty even, demonstrating that tiny living appeals to people of all ages.
- Around 2 out of 5 homeowners are over the age of 50.
- About 2 out of 5 homeowners are between 30 and 50.
- Approximately 1 in 5 homeowners are under the age of 30.
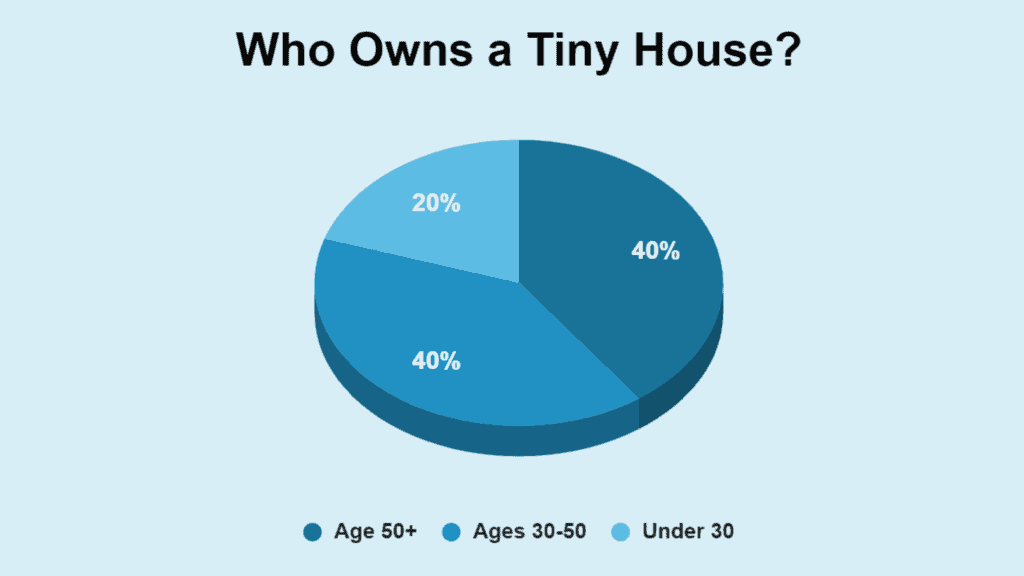
| Age Group | Proportion of Homeowners |
|---|---|
| Over 50 years old | 2 out of 5 |
| Between 30 and 50 | 2 out of 5 |
| Under 30 | 1 out of 5 |
Source: The Tiny Life
Tiny Homeowner Gender
Women are marginally more inclined to own tiny homes than men, with 55% of tiny homes owned by women. This indicates a trend toward more women embracing the tiny living movement, possibly due to the appeal of a simpler, more manageable living space and the financial freedom that tiny homes provide.
The tiny living movement has gained approval among people seeking a more sustainable and cost-effective lifestyle, and it is interesting to see this reflected in the gender distribution of tiny homeowners.
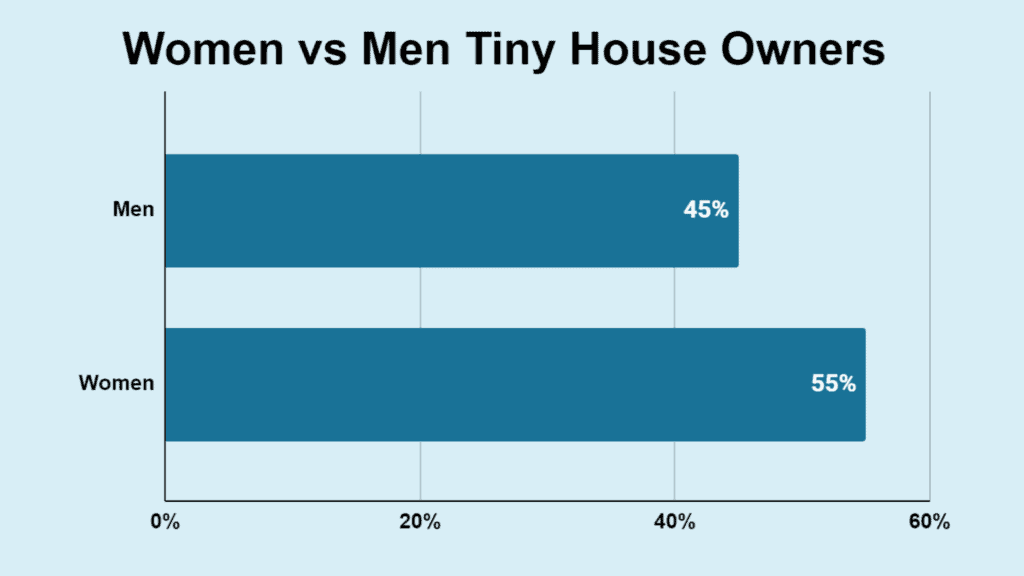
| Gender | Tiny Homeowners |
|---|---|
| Female | 55% |
| Male | 45% |
Source: The Tiny Life
Income of Tiny Homeowners
The average American income in 2023 varied depending on the source and the specific metric (e.g., median household income, average annual salary, etc.). Taking this into consideration:
- The annual average wage across the U.S. is $59,428.
- U.S. families with two people had an annual median income of $75,143 in 2023.
- The average income of a tiny home occupant is around $42,038.
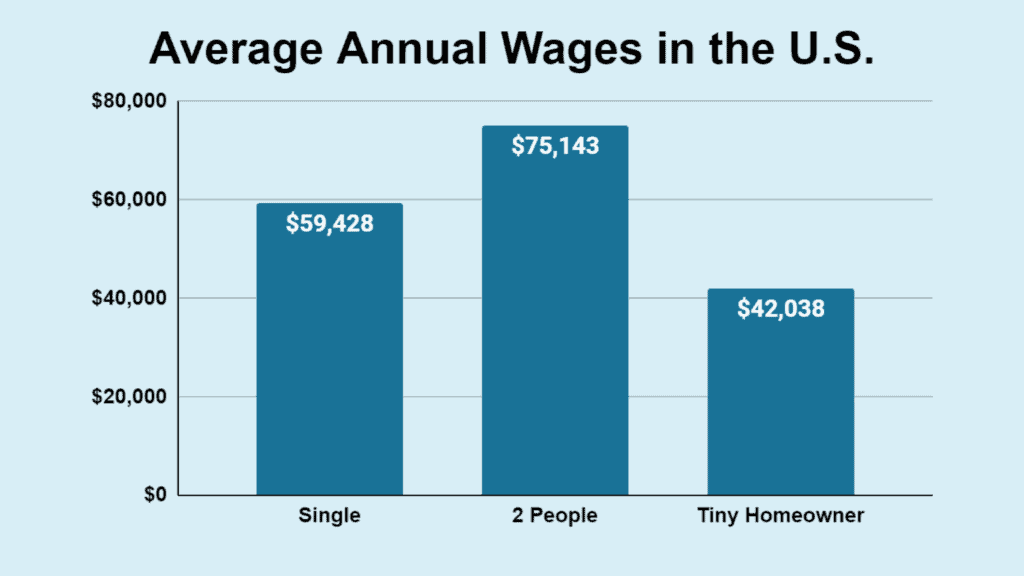
| Type of Earner(s) | Annual Income |
|---|---|
| Single | $59,428 |
| Double | $75,143 |
| Tiny House Owner | $42,038 |
Sources: Forbes, Demand Sage, US Census Bureau, Ruby Home
Mortgage Status of Tiny Homeowners
A higher proportion of tiny homeowners are mortgage-free than traditional homeowners, highlighting the financial benefits of tiny living.
This difference indicates that a tiny house can offer more financial freedom and less debt, as homeowners are not tied to long-term financial commitments and can pay off their homes more quickly.
Overall, tiny living emerges as a more affordable and financially liberating housing option.
- 68% of tiny homeowners have no mortgage.
- 29.3% of all homeowners in the U.S. are mortgage-free.
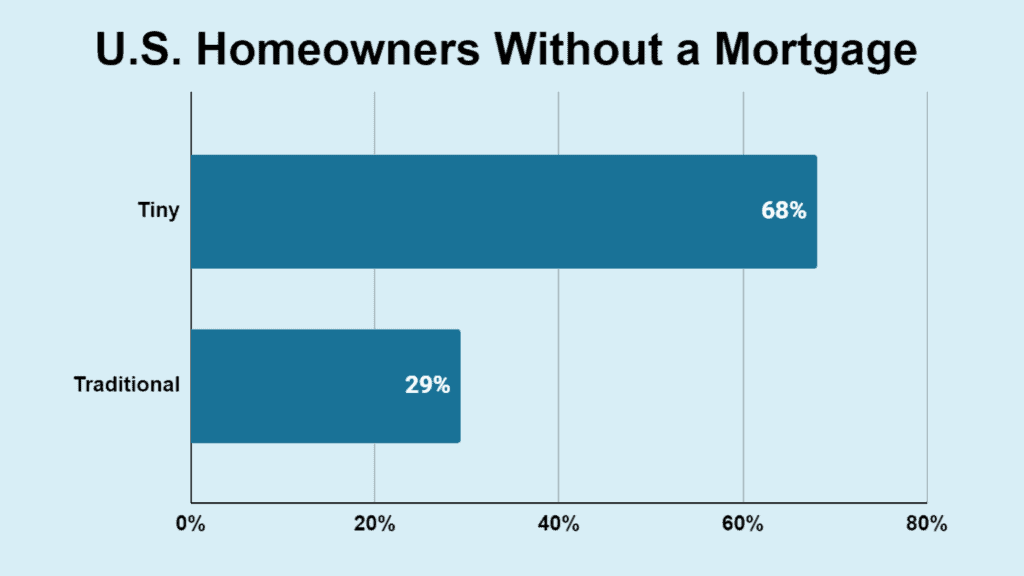
| Type of Home | No Mortgage |
|---|---|
| Tiny | 68% |
| Conventional | 29.3% |
Source: The Tiny Life
Tiny Homeowner Finances
Adopting a tiny living lifestyle can result in greater financial stability and an increased ability to save money.
The reduced living expenses associated with tiny homes, such as lower utility bills, minimal maintenance costs, and the possibility of living mortgage-free, contribute to this financial advantage.
As a result, tiny homeowners can often allocate more of their income toward savings, investments, and other financial goals, ultimately enhancing their overall financial well-being. Tiny living can lead to less financial stress and more economic security.
- A significant 55% of individuals residing in tiny homes have accumulated more savings than the average American.
- 89% of tiny homeowners have less credit card debt than the typical person in the U.S.
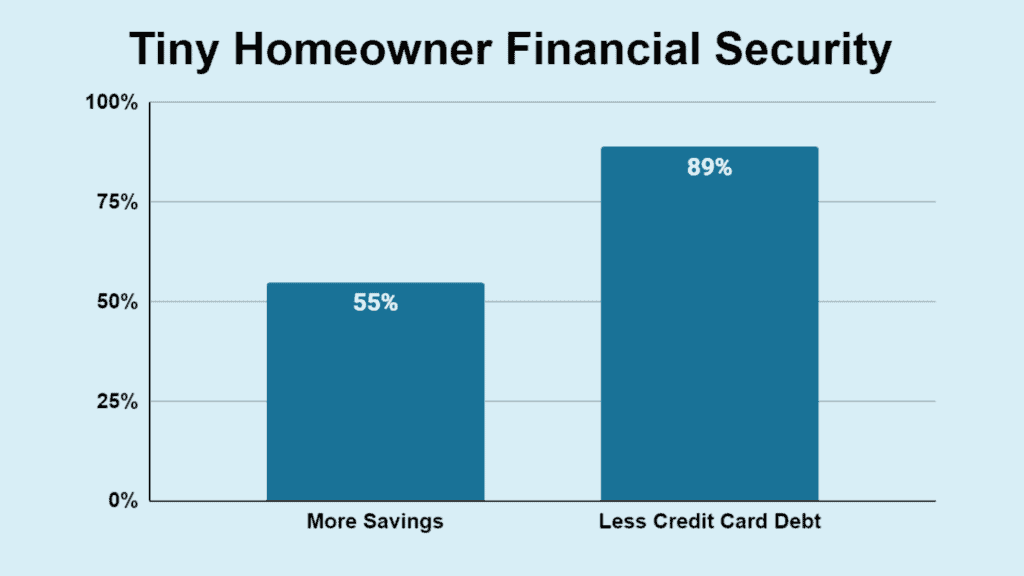
| Tiny Homeowners | Percentage |
|---|---|
| More Savings | 55% |
| Less Credit Card Debt | 89% |
Source: The Tiny Life
Tiny Home Resale Value
It’s rare for people to recuperate their entire investment if they sell their tiny homes. This is something to consider when deciding to live in a tiny house.
Tiny homes tend to depreciate faster than traditional homes for several reasons:
- Limited Market: The tiny home market is smaller than traditional homes, which can make them harder to sell and decrease their value over time.
- Wear and Tear: Tiny homes are often built on trailers and can be moved from place to place. This mobility can lead to more degradation, decreasing the home’s value.
- Quality of Construction: Some tiny homes are built by their owners or builders who may follow different construction standards than traditional home builders. This can result in lower-quality homes that depreciate faster.
- Land Ownership: Traditional homes typically come with land, which can appreciate over time and add to the home’s value. Tiny houses are often placed on rented land or land owned by someone else, which can limit their appreciation potential.
- Financing and Insurance: It can be more challenging to secure the funding and insurance for a tiny home, limiting its value and appeal to potential buyers.
- Zoning and Building Codes: Tiny homes often face zoning and building code challenges that can limit where they can be placed and how they can be used.
Overall, while tiny homes can offer many benefits, their unique characteristics can also lead to faster depreciation compared to traditional houses.
Source: Porch
Conclusion
The tiny home market in the U.S. is thriving, with a growing number of people choosing to live in tiny homes for financial, environmental, and lifestyle reasons.
The data shows that tiny living appeals to many demographics and can provide significant financial benefits. However, it’s essential to consider the potential downsides, such as the higher cost per square foot and the depreciation of tiny homes over time.
In Addition
The growing popularity of tiny homes in the U.S. is a significant part of the evolving landscape of American housing. This trend toward smaller, more affordable living spaces reflects a shift in priorities for many people. It’s interesting to explore the broader perspective on housing in the U.S. and insights into homeownership rates nationwide.
Additionally, understanding the state of mortgages in the U.S. is crucial for anyone considering homeownership, whether in a tiny or traditional home. Our exploration of tiny homes provides a well-rounded view of the current housing market and its financial implications.